“Building the Infinite Internet” by Scott Woolley, April 23, 2007
http://www.forbes.com/free_forbes/2007/0423/068.html
As the internet continues to grow in size, there is a greater and greater need to find efficient ways to transfer data between servers and computers. According to the article, Akamai Technologies Inc. provides methods to overcome some of the archaic rules of the internet to accommodate the need for speed with increasingly larger demand on the network. The article comments on three typical problems the internet may encounter that Akamai claims to solve (in the sidebar “A More Clever Internet”).
1. Flash Crowds: A large amount of users from all around the world try to access the same site or file, swamping the server that holds this data.
2. Fat File Paradox: With the increasing use of the internet to transfer very large files such as movies, a large amount of time is wasted on confirmation messages between computers after sending only 128,000 bits.
3. Line Cuts: When certain internet lines fail or are cut (such as when undersea cables snapped due to the recent tsunami), files get lost and it takes awhile for internet servers to find new paths to other computers.
Akamai’s solution to all three of these problems is to provide a shorter path then already available on the internet. The picture below shows the concept used:
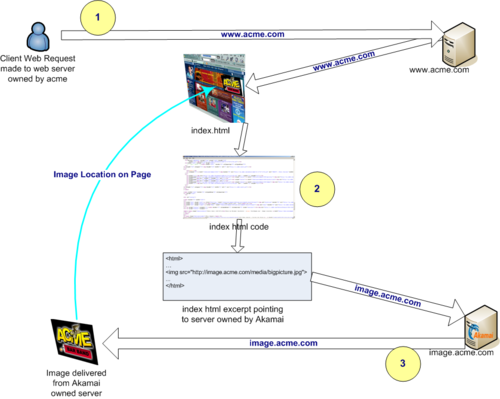
In essence, Akamai servers monitor their clients’ websites and determine how data could travel more efficiently. They do this by creating a new shortest path in the network. For example, in the case of the flash crowd problem, if the Akamai servers determine that there is a high demand for a certain picture in New York City from a website they serve in Los Angeles, they will copy the picture and store it in a server located near New York City. Therefore, all users in New York City were provided a new shorter path to the information they demand. In this way, traffic build up is avoided and information travels a shorter path to the users. This technique basically tries to find and create shorter paths on the internet in real-time, to meet the current demands on internet.


* You can follow any responses to this entry through the RSS 2.0 feed.